What is Tinnitus? Symptoms, Causes, and Types Explained
Tinnitus, often described as a ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ears, is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it’s commonly perceived as a simple annoyance, it can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Understanding what tinnitus is, its symptoms, causes, and the various types can help those affected navigate their experiences and seek appropriate treatment.
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is not a disease but a symptom of an underlying condition. It can manifest in one or both ears and varies in intensity, from a faint sound that’s easy to ignore to a loud noise that can be debilitating. For some, tinnitus may be a constant presence, while for others, it might come and go.
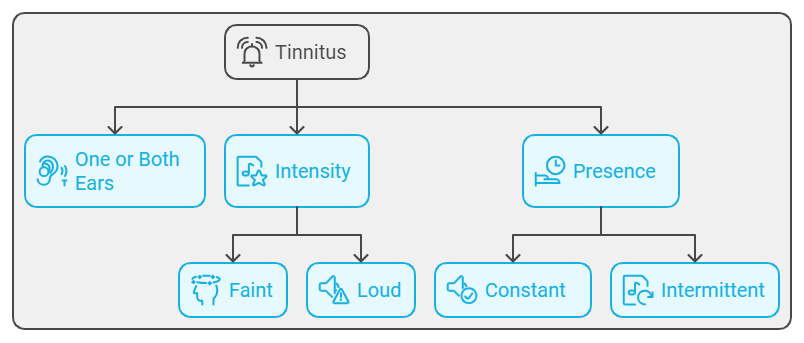
Symptoms of Tinnitus
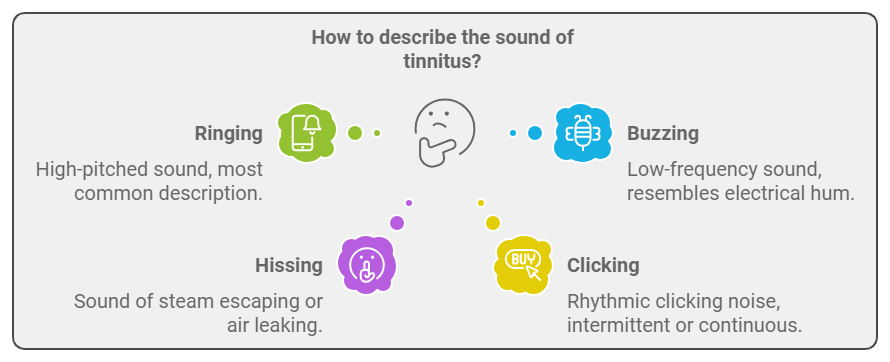
The hallmark symptom of tinnitus is hearing a sound that has no external source. This sound can vary widely among individuals and may include:
- Ringing: The most common description of tinnitus, resembling a high-pitched ringing sound.
- Buzzing: A low-frequency buzzing sound that can resemble an electrical hum.
- Hissing: Similar to the sound of steam escaping or air leaking from a tire.
- Clicking: A rhythmic clicking noise, which can be intermittent or continuous.
- Roaring: A deep, powerful sound that may feel overwhelming.
The experience of tinnitus can be subjective; what one person perceives may be entirely different for another. Some people report that their symptoms are worsened by stress, fatigue, or exposure to loud noises.
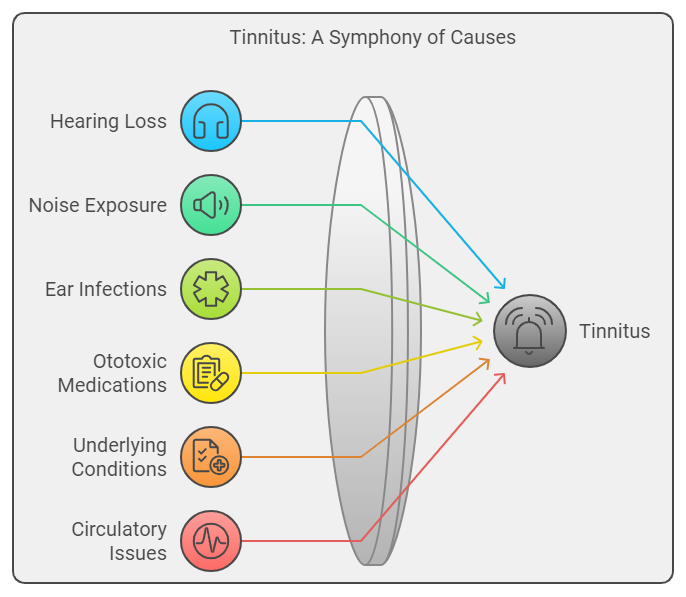
Causes of Tinnitus
Understanding the causes of tinnitus is crucial in determining the best approach for treatment. Tinnitus can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Hearing Loss: Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis) is one of the most common causes. As we age, the delicate hair cells in the cochlea of the inner ear can become damaged, leading to auditory issues and tinnitus.
- Noise Exposure: Prolonged exposure to loud sounds, such as music concerts, heavy machinery, or gunfire, can damage hearing and lead to tinnitus. Even short bursts of intense noise can have lasting effects.
- Ear Infections and Blockages: Ear infections, wax buildup, or foreign objects in the ear can create pressure and affect hearing, often resulting in tinnitus.
- Ototoxic Medications: Some medications can be harmful to the inner ear. Common culprits include certain antibiotics, diuretics, and chemotherapy drugs.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Conditions like Ménière’s disease, acoustic neuroma, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can also lead to tinnitus.
- Circulatory Issues: Conditions that affect blood flow, such as high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, or anemia, can contribute to pulsatile tinnitus, where the ringing is synchronized with the heartbeat.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms. The relationship is bidirectional—while tinnitus can cause stress, stress can also heighten the perception of tinnitus.
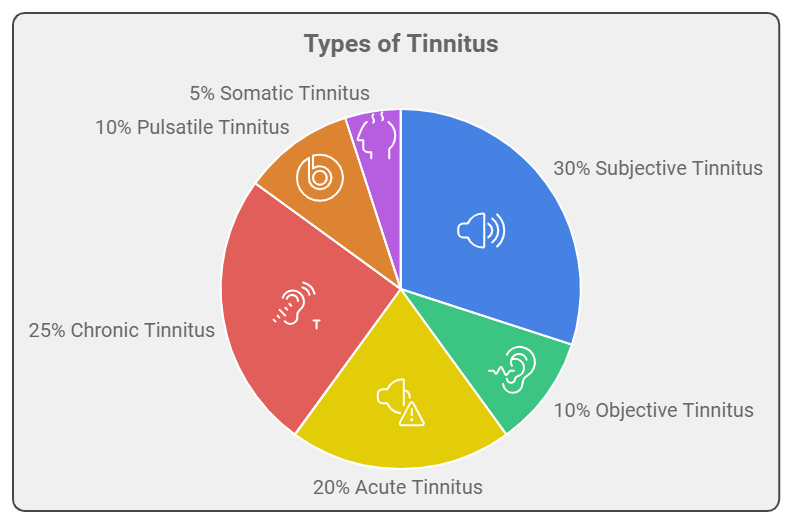
Types of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can be categorized into different types based on its characteristics and underlying causes:
- Subjective Tinnitus: This is the most common type, where only the affected person can hear the sounds. It can vary greatly in tone, intensity, and duration.
- Objective Tinnitus: A rare form that can be heard by a doctor during an examination, often due to a physical condition affecting the ear or the auditory pathway.
- Acute Tinnitus: Refers to tinnitus that appears suddenly and can be temporary. It often resolves on its own within a short period.
- Chronic Tinnitus: When tinnitus persists for six months or longer, it is classified as chronic. This type can be more challenging to manage and may require ongoing treatment.
- Pulsatile Tinnitus: This type is characterized by rhythmic sounds that often align with the heartbeat. It may indicate a vascular issue or other underlying condition.
- Somatic Tinnitus: This type is influenced by physical factors such as head or neck movements. Some people find that changing their posture or moving their head can alter the sound of their tinnitus.
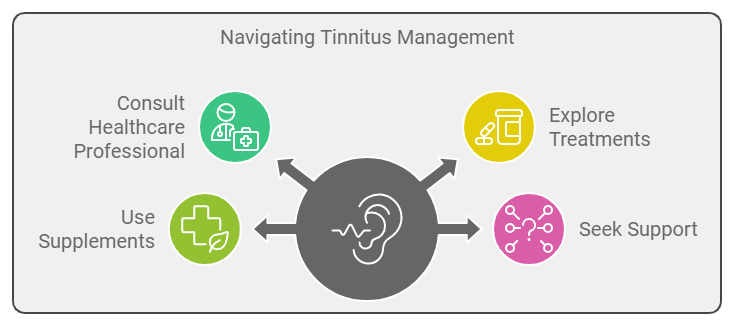
Living with Tinnitus !!
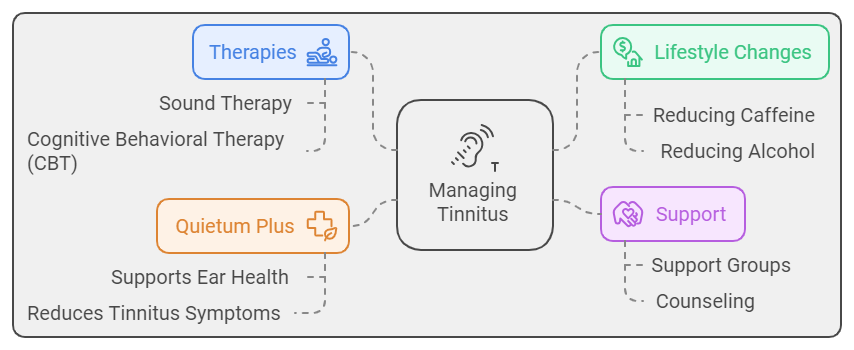
For those experiencing tinnitus, it can often feel isolating and frustrating. However, it’s essential to know that there are resources and strategies available. Many people find relief through sound therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), or lifestyle changes such as reducing caffeine and alcohol intake. Support groups and counseling can also provide valuable emotional support.
Quietum Plus supplement
Additionally, if you’re looking for a more targeted approach to managing tinnitus, consider exploring Quietum Plus, a natural supplement designed to support ear health and reduce tinnitus symptoms. Formulated with ingredients known for their beneficial effects on hearing, Quietum Plus may help alleviate the ringing and buzzing that so many experience. Many users have reported positive results, finding it to be a helpful addition to their tinnitus management plan.

Conclusion
Tinnitus is a complex condition that can significantly affect daily life. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and types, individuals can better advocate for their health and seek appropriate help. If you or someone you know is experiencing tinnitus, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to explore potential treatments and coping strategies. While tinnitus may be a challenging journey, support and resources are available to help navigate its effects, allowing individuals to reclaim their quality of life. And remember, incorporating supplements like Quietum Plus into your routine may offer an additional layer of relief, helping you on your path to better ear health.